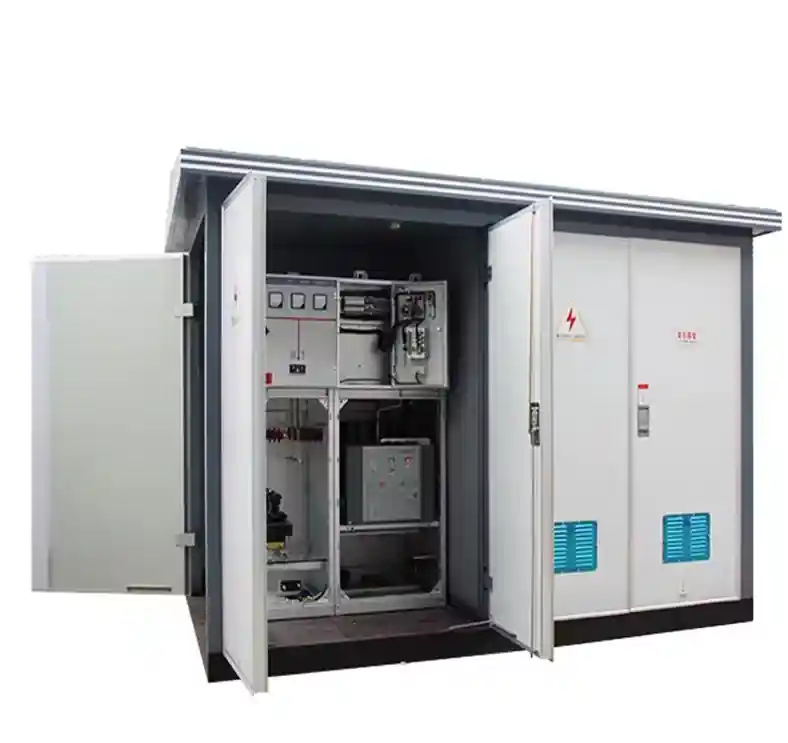
In the world of electrical power distribution, temporary substations serve a critical role in maintaining grid stability, supporting project continuity, and ensuring uninterrupted service during outages or transitions. Whether deployed during emergency situations, major construction works, or as a stopgap during permanent infrastructure upgrades, these substations are engineered for quick deployment, flexibility, and performance under dynamic conditions.
What Is a Temporary Substation?
A temporary substation is a mobile or semi-permanent power facility designed to perform the same fundamental functions as a permanent substation—transforming voltage levels, enabling switching, and ensuring protection of electrical systems. However, unlike fixed substations, temporary ones are prefabricated, modular, and designed for rapid deployment and removal.
They typically include:
- Medium or high voltage switchgear
- Power transformers (e.g., 11kV/33kV to 400V/230V)
- Protection and control systems
- Mobile enclosures or trailer-mounted platforms

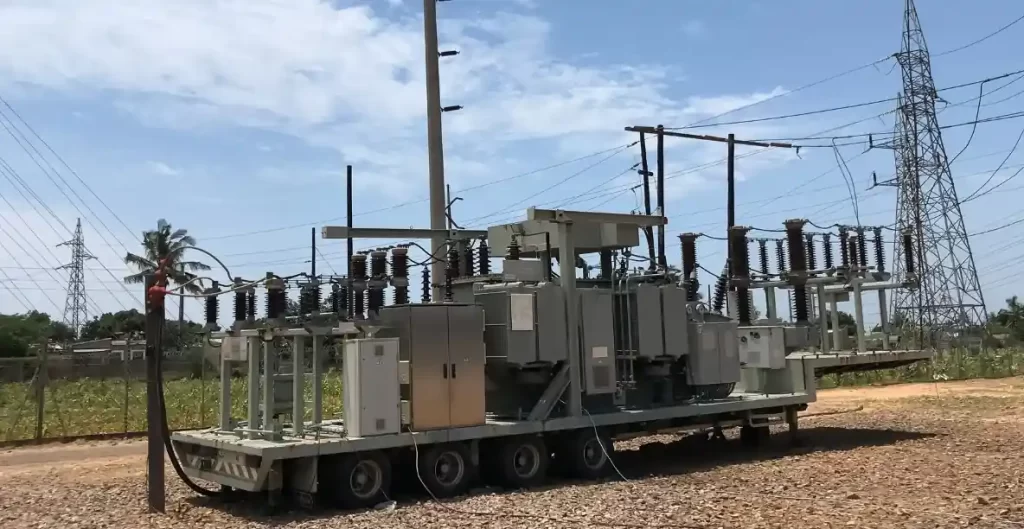
Application Areas of Temporary Substations
Temporary substations are widely used in scenarios where agility, speed, and mobility are essential:
- Construction Projects: To provide power to large-scale building or infrastructure sites
- Utility Grid Maintenance: Backup power during substation upgrades or repairs
- Disaster Relief: Emergency power in response to natural disasters or power outages
- Events and Festivals: Temporary electricity supply for outdoor venues
- Remote Industrial Sites: Mining operations, oil fields, and mobile drilling rigs

Market Trends and Background
According to recent reports from IEEMA and Global Substation Market Insights, the demand for temporary substations is rising sharply due to growing investments in infrastructure, increasing grid modernization activities, and the expanding footprint of renewable energy projects.
The IEEE also recognizes mobile electrical substation guide as a key part of disaster-resilient power infrastructure—especially in regions prone to extreme weather events. Leading manufacturers like ABB, Schneider Electric, and Siemens are developing compact, intelligent solutions with features like remote monitoring, IoT-based diagnostics, and SCADA integration.
See more technical definitions at Wikipedia – Electrical Substation.
Technical Specifications
A standard temporary substation can be customized based on voltage level and capacity requirements. Below is a typical configuration:
| Component | Specification Example |
|---|---|
| Voltage Rating | 11kV / 22kV / 33kV primary |
| Transformer Capacity | 500 kVA – 5 MVA |
| Secondary Voltage | 400V / 230V |
| Mobility | Trailer-mounted or containerized |
| Cooling System | ONAN or ONAF |
| Enclosure Type | IP54–IP65, suitable for outdoor use |
| Standards | IEC 60076, IEC 62271, IEEE C57 |
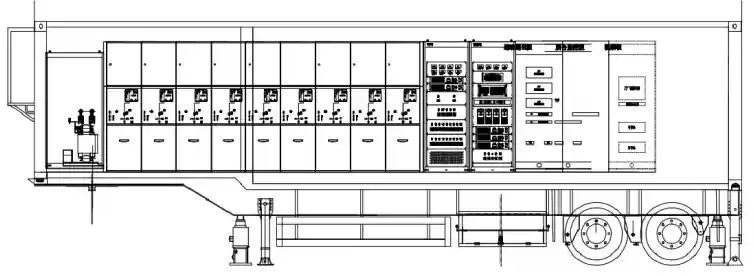
Comparison: Temporary vs. Permanent Substations
| Aspect | Temporary Substation | Permanent Substation |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment Time | Days to weeks | Months to years |
| Cost | Lower upfront; rental options | Higher capital investment |
| Flexibility | High (relocatable) | Fixed location |
| Service Duration | Short- to mid-term use | Long-term infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Lower complexity | More robust systems |
While not designed for long-term operation, temporary substations are often used during the commissioning or renovation phases of large power projects.
Selection Tips: Choosing the Right Temporary Substation
When selecting a temporary substation, keep the following in mind:
- Load Requirements: Estimate current and peak loads to match transformer rating.
- Mobility Needs: Trailer-mounting is ideal for frequent relocation.
- Environmental Conditions: Ensure the unit can withstand dust, humidity, or temperature extremes.
- Grid Compatibility: Match input/output voltage and protection schemes with the local grid.
- Vendor Support: Choose suppliers that offer on-site installation, commissioning, and technical assistance.
Reputed brands like PINEELE, ABB, and Eaton offer rental and turnkey solutions with full compliance to IEC and IEEE standards.
Authoritative References
- IEEE Std C37™ Series: Protection and control for substations
- IEC 62271-202: Prefabricated HV/LV substations
- ABB White Paper: Mobile substations for emergency and temporary power
- Wikipedia – Substation Types
These references offer technical validation and background necessary for infrastructure engineers and procurement teams.
FAQs
A: Depending on site conditions, a temporary substation can be installed and commissioned within 3–10 days, compared to months for permanent solutions.
A: Yes. When designed per IEC or IEEE standards, they include grounded enclosures, arc protection, and automatic trip mechanisms.
A: While they are not designed for permanent use, some modular units can be upgraded or integrated into permanent setups with additional engineering support.
A temporary Substation guide is a versatile, rapid-deployment solution ideal for meeting short- to medium-term power distribution needs. Whether you’re facing a natural disaster, undergoing facility upgrades, or powering a remote industrial site, this type of substation offers reliability, scalability, and compliance with global standards.


