Core Concept: What Defines a Small Substation?
A small substation—also known as a compact substation or mini substation—is a fully integrated power distribution unit that includes:
- Medium-voltage switchgear
- Distribution transformer
- Low-voltage panel
- All housed within a weatherproof, factory-assembled enclosure
These substations typically handle 100 kVA to 2500 kVA and operate within 11kV, 22kV, or 33kV systems. Their compact, plug-and-play design enables quick installation and minimal civil work, making them ideal for fast-growing urban and rural areas.
Applications of Small Substations
Small substations are widely used in:
- Residential and Commercial Buildings
Providing step-down voltage to 400V for domestic or office use - Industrial Sites
Powering small-scale machinery or local process units - Renewable Energy Plants
Acting as the point of interconnection between solar or wind farms and the utility grid - Mobile Power Units
Used in mining, oilfields, and temporary construction projects - Remote or Rural Electrification
Bringing power to areas where grid expansion is limited
Market Trends and Background
As per IEEMA and IEA reports, demand for small substations is increasing globally due to:
- Rapid urbanization and rural electrification programs
- Growth in rooftop solar and microgrid installations
- Increased reliance on distributed energy systems
- Smart city development projects
Small substations, especially prefabricated and skid-mounted types, are a key component of decentralized energy strategies, providing reliable local power without the footprint of full-scale substations.
According to Wikipedia, compact substations are part of a broader push to improve energy efficiency and reduce losses during last-mile delivery.
Technical Specifications at a Glance
| Component | Typical Range / Value |
|---|---|
| Rated Voltage | 11kV / 22kV / 33kV |
| Transformer Capacity | 100 – 2500 kVA |
| LV Output Voltage | 400V / 415V |
| Frequency | 50Hz / 60Hz |
| Protection Class | IP44 – IP65 |
| Enclosure Type | Outdoor metal-clad or kiosk type |
| Cooling Type | Oil-immersed or dry-type transformer |
| Standards Compliance | IEC 62271, IEC 60076, IEEE C57 |
Small vs Large Substations: What’s the Difference?
| Feature | Small Substation | Large Substation |
|---|---|---|
| Power Capacity | 100 – 2500 kVA | Above 5000 kVA |
| Voltage Levels | Up to 33kV | Up to 400kV or more |
| Footprint | Compact (1–3 m²) | Large area (multiple buildings) |
| Installation Time | 1–2 days | Weeks or months |
| Applications | Local distribution | Regional grid control |
| Customization | Limited | Highly customizable |
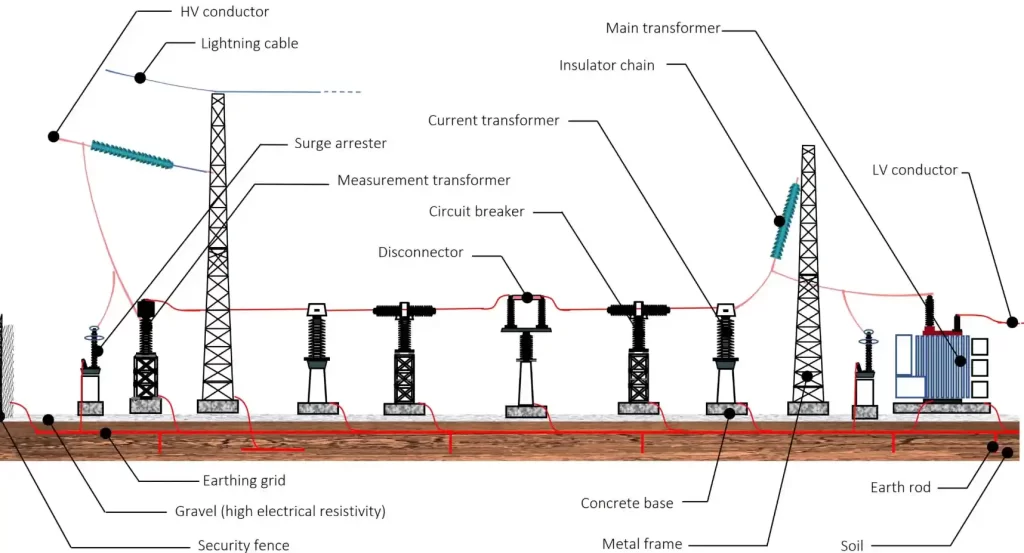
Buying Tips: How to Select a Small Substation
When choosing a small substation, consider:
- Load Requirement: Determine transformer size based on peak load (in kVA).
- Environment: Choose enclosure with IP54+ rating for dusty or humid areas.
- Type of Transformer:
- Oil-immersed: More efficient and cost-effective
- Dry-type: Safer indoors and for fire-sensitive zones
- Protection Systems: Ensure the LV panel includes MCCBs, surge protectors, and metering.
- Mobility: For temporary use, skid-mounted or trailer-mounted units are ideal.
Reputable suppliers such as ABB, Schneider Electric, Siemens, and emerging manufacturers like PINEELE offer a wide range of IEC/ANSI-certified compact substations.
Cited & Recommended Sources
- IEEE C57 Series – Transformer Standards
- Wikipedia: Electrical Substation
- ABB Compact Secondary Substations
- IEEMA Reports – Indian Substation Development
Frequently Asked Questions
A: With proper maintenance, small substations can last 25–30 years, depending on environmental conditions and component quality.
A: Yes, they are commonly used to step up or step down voltage in solar PV systems and are ideal for hybrid energy applications.
A: Most units are factory-assembled and delivered ready for use. They are placed using a crane and connected within hours, minimizing site work.
A small substation guide is more than just a miniature version of a conventional power hub—it is a highly practical, efficient, and scalable solution for modern electricity distribution. Whether it’s for a housing development, a solar farm, or a temporary industrial site, compact substations provide the backbone of localized energy systems.
By understanding the components, standards, and configuration options, engineers and decision-makers can choose the right solution that balances cost, performance, and reliability.


