Dans le monde de la distribution de l'énergie électrique, sous-stations temporaires jouent un rôle essentiel dans le maintien de la stabilité du réseau, dans la continuité des projets et dans la garantie d'un service ininterrompu pendant les pannes ou les transitions. Qu'elles soient déployées dans des situations d'urgence, lors de grands travaux de construction ou comme palliatif lors de mises à niveau permanentes de l'infrastructure, ces sous-stations sont conçues pour un déploiement rapide, une grande flexibilité et des performances dans des conditions dynamiques.
Qu'est-ce qu'une station temporaire ?
A temporaire sous-station est une installation électrique mobile ou semi-permanente conçue pour remplir les mêmes fonctions fondamentales qu'une sous-station permanente : transformer les niveaux de tension, permettre la commutation et assurer la protection des systèmes électriques. Cependant, contrairement aux postes fixes, les postes temporaires sont préfabriqué, modulaireet conçu pour un déploiement et un retrait rapides.
Il s'agit généralement des éléments suivants
- Appareils de commutation à moyenne ou haute tension
- Transformateurs de puissance (par exemple, 11kV/33kV à 400V/230V)
- Systèmes de protection et de contrôle
- Enceintes mobiles ou plates-formes montées sur remorque
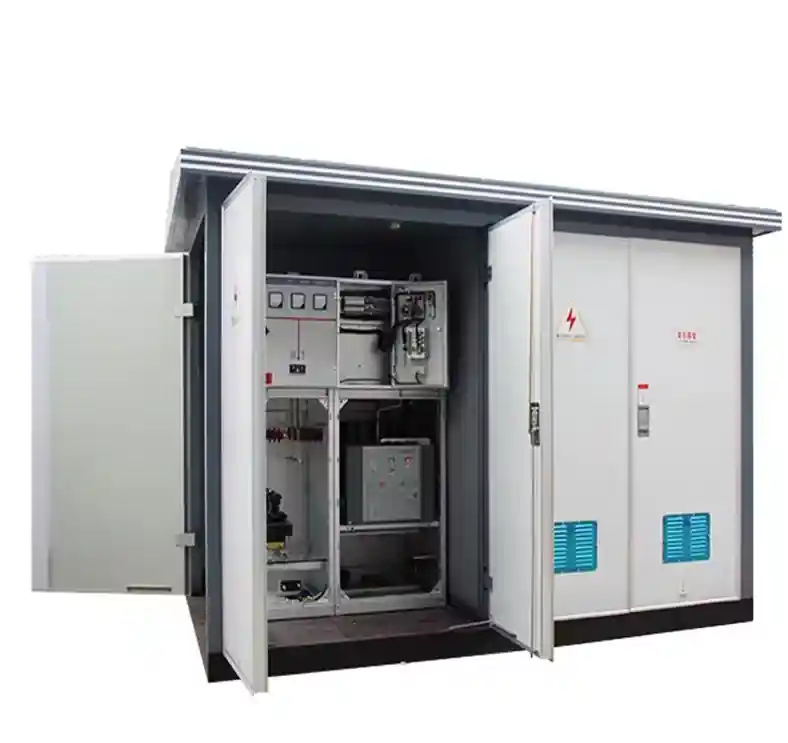

Domaines d'application des sous-stations temporaires
Les sous-stations temporaires sont largement utilisées dans des scénarios où l'agilité, la vitesse et la mobilité sont essentielles :
- Projets de construction: Fournir de l'énergie à des sites de construction ou d'infrastructure à grande échelle
- Maintenance du réseau de distribution: Alimentation de secours pendant les mises à niveau ou les réparations des sous-stations
- Aide en cas de catastrophe: Alimentation de secours en cas de catastrophe naturelle ou de panne d'électricité
- Événements et festivals: Alimentation électrique temporaire pour les sites en plein air
- Sites industriels isolés: Exploitations minières, champs pétroliers et plates-formes de forage mobiles
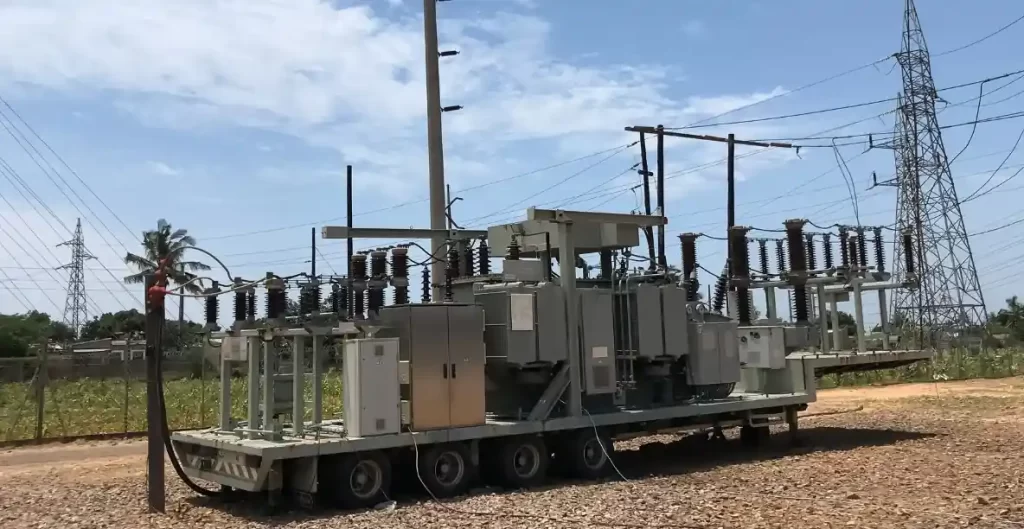

Tendances du marché et contexte
Selon des rapports récents de IEEMA et Aperçus du marché mondial des sous-stationsLa demande de sous-stations temporaires augmente fortement en raison de l'accroissement des investissements dans les infrastructures, de l'augmentation des activités de modernisation des réseaux et de l'expansion des projets d'énergie renouvelable.
Le IEEE reconnaît également les téléphones mobiles guide des postes électriques en tant qu'élément clé de la une infrastructure électrique résistante aux catastrophes-en particulier dans les régions sujettes à des phénomènes météorologiques extrêmes. Des fabricants de premier plan comme ABB, Schneider Electricet Siemens développent des solutions compactes et intelligentes dotées de caractéristiques telles que surveillance à distance, Diagnostics basés sur l'IdOet Intégration SCADA.
Pour plus de détails sur les définitions techniques, voir Wikipedia - Poste électrique.
Spécifications techniques
Une sous-station temporaire standard peut être personnalisée en fonction du niveau de tension et des exigences de capacité. Vous trouverez ci-dessous une configuration typique :
| Composant | Exemple de spécification |
|---|---|
| Tension nominale | 11kV / 22kV / 33kV primaire |
| Capacité du transformateur | 500 kVA - 5 MVA |
| Tension secondaire | 400V / 230V |
| Mobilité | Monté sur remorque ou en conteneur |
| Système de refroidissement | ONAN ou ONAF |
| Type de boîtier | IP54-IP65, utilisable en extérieur |
| Normes | IEC 60076, IEC 62271, IEEE C57 |
Comparaison : Sous-stations temporaires et permanentes
| Aspect | Sous-station temporaire | Sous-station permanente |
|---|---|---|
| Temps de déploiement | De quelques jours à quelques semaines | Des mois aux années |
| Coût | Moins de frais initiaux ; options de location | Augmentation de l'investissement en capital |
| Flexibilité | Haut (déplaçable) | Lieu fixe |
| Durée du service | Utilisation à court et moyen terme | Infrastructures à long terme |
| Maintenance | Moins de complexité | Des systèmes plus robustes |
Bien qu'elles ne soient pas conçues pour une exploitation à long terme, les sous-stations temporaires sont souvent utilisées pendant les phases de mise en service ou de rénovation des grands projets énergétiques.
Conseils de sélection : Choisir le bon poste temporaire
Lors de la sélection d'une sous-station temporaire, il convient de garder à l'esprit les éléments suivants :
- Exigences en matière de charge: Estimer le courant et les charges de pointe en fonction de la puissance du transformateur.
- Besoins de mobilité: Le montage sur remorque est idéal pour les déplacements fréquents.
- Conditions environnementales: Assurez-vous que l'appareil peut résister à la poussière, à l'humidité ou à des températures extrêmes.
- Compatibilité de la grille: Faire correspondre la tension d'entrée/sortie et les schémas de protection avec le réseau local.
- Soutien aux fournisseurs: Choisissez des fournisseurs qui proposent une installation sur site, une mise en service et une assistance technique.
Des marques réputées comme PINEELE, ABBet Eaton offrent des solutions de location et des solutions clés en main dans le respect total des normes de l'UE. CEI et IEEE normes.
Références autorisées
- Série IEEE Std C37™: Protection et contrôle des postes électriques
- IEC 62271-202: Postes préfabriqués HT/BT
- Livre blanc d'ABB: Sous-stations mobiles pour l'alimentation d'urgence et temporaire
- Wikipedia - Types de postes
Ces références offrent la validation technique et le contexte nécessaires aux ingénieurs en infrastructures et aux équipes chargées des achats.
FAQ
A : Selon les conditions du site, une sous-station temporaire peut être installée et mise en service en 3 à 10 jours, contre plusieurs mois pour les solutions permanentes.
A : Oui. Lorsqu'il est conçu par CEI ou IEEE Ils comprennent des enceintes avec mise à la terre, une protection contre les arcs électriques et des mécanismes de déclenchement automatique.
A : Bien qu'elles ne soient pas conçues pour une utilisation permanente, certaines unités modulaires peuvent être mises à niveau ou intégrées dans des installations permanentes avec un soutien technique supplémentaire.
A temporaire Guide des sous-stations est une solution polyvalente à déploiement rapide, idéale pour répondre aux besoins de distribution électrique à court et moyen terme. Qu'il s'agisse de faire face à une catastrophe naturelle, de moderniser des installations ou d'alimenter un site industriel éloigné, ce type de sous-station offre les avantages suivants fiabilité, évolutivitéet conformité avec les normes mondiales.


