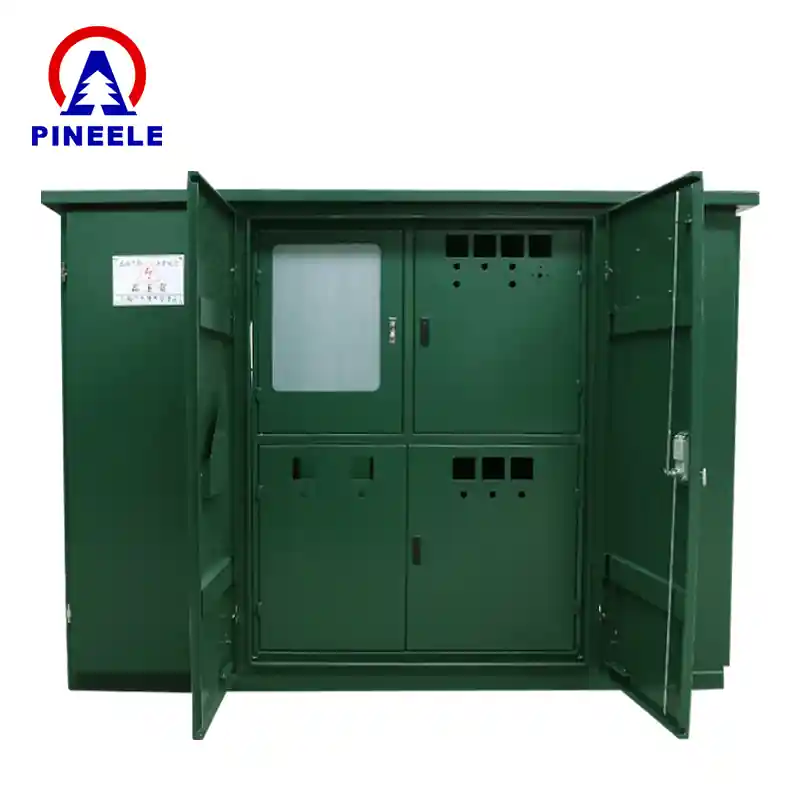
Introduction au poste 220 kV
A 220 kV sous-station est une installation électrique à haute tension utilisée pour la production d'électricité. transmission et distribution d'énergie électrique à un niveau de tension de 220 kilovolts. Il joue un rôle essentiel dans le réseau en abaissant la tension des niveaux de transmission (souvent 400 kV ou plus) à des tensions plus basses (comme 132 kV, 66 kV ou 33 kV) pour la distribution ultérieure. Cette infrastructure garantit une fourniture d'électricité efficace, fiable et sûre dans de vastes zones géographiques.
Applications et importance
Les sous-stations de 220 kV sont essentielles dans :
- Réseaux électriques nationauxsurtout dans les pays dotés d'une infrastructure à grande échelle.
- Zones industrielles nécessitant des charges énergétiques élevées.
- Centres urbains où la demande d'électricité est constamment élevée.
- Installations de production d'énergie renouvelablenotamment les parcs solaires et éoliens raccordés au réseau à haute tension.
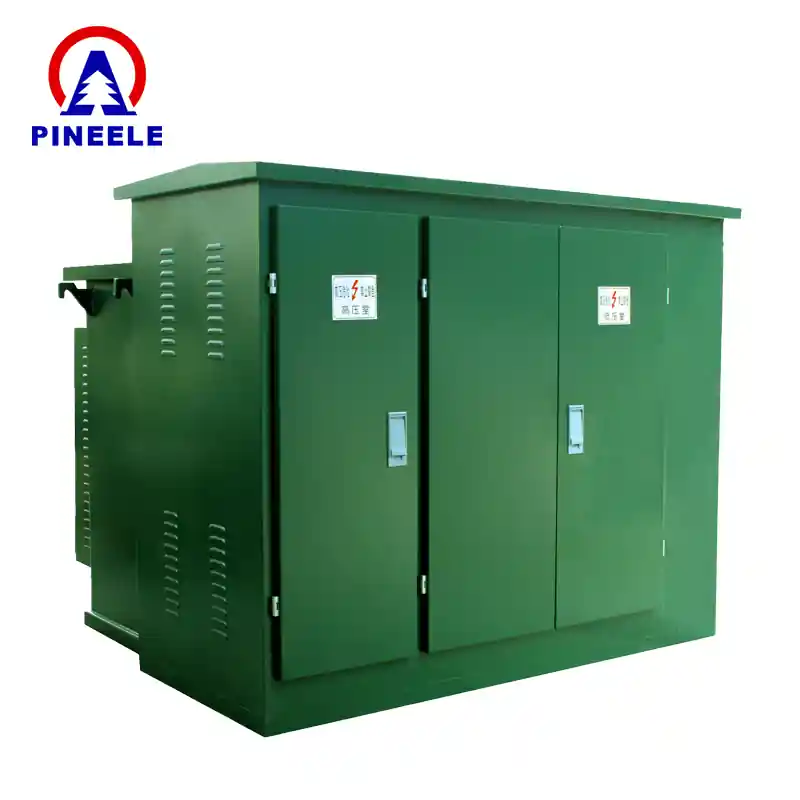

Ces sous-stations assurent régulation de la tension, isolation des défautsL'énergie électrique est une source d'énergie renouvelable et sûre, qui assure la continuité des opérations pour les industries et les services publics.
Tendances du marché et contexte industriel
Selon la Agence internationale de l'énergie (AIE) et des données de IEEMA (Association indienne des fabricants de produits électriques et électroniques)La demande de postes à haute tension (220 kV par exemple) augmente en raison des facteurs suivants :
- Accroître l'intégration des énergies renouvelables.
- Expansion des réseaux intelligents.
- Urbanisation et croissance industrielle dans les régions en développement.
En 2024, les investissements mondiaux dans les infrastructures de transport ont dépassé les $300 milliards, les sous-stations de 220 kV contribuant de manière significative à la stabilité régionale et à l'équilibrage de la charge.
Spécifications techniques
| Paramètres | Valeur typique |
|---|---|
| Tension nominale | 220 kV |
| Fréquence nominale | 50/60 Hz |
| Capacité du transformateur | 100 MVA - 500 MVA |
| Configuration du système | Double jeu de barres / Disjoncteur et demi |
| Type d'isolation | AIS (isolation par l'air) / GIS (isolation par le gaz) |
| Disjoncteurs | SF6, vide ou huile |
| Système de protection | Automatisation à relais et SCADA |
| Capacité de résistance aux pannes | Jusqu'à 40 kA pendant 3 secondes |
AIS vs GIS dans les sous-stations 220 kV
Il existe deux types de postes 220 kV :
- AIS (Air-Insulated Substation):
Utilise l'air comme moyen d'isolation. Économique, facile à entretenir, mais nécessite plus d'espace. - GIS (poste isolé au gaz):
Utilisations Gaz SF6 pour l'isolation. Compact, résistant aux intempéries, idéal pour les zones urbaines où l'espace est limité. Coût initial plus élevé mais entretien moindre.
Différences par rapport aux postes à basse tension
| Fonctionnalité | Sous-station 220 kV | Sous-station 132 kV / 66 kV |
|---|---|---|
| Niveau de tension | Très haute tension | Haute tension |
| Capacité du transformateur | Plus élevé | Moyen |
| Position de la grille | Niveau de transmission | Niveau de distribution |
| Coût | Haut | Moyen |
| Empreinte | Plus grand / compact (GIS) | Plus petit |
Guide de sélection et conseils d'achat
Lors de la sélection d'un poste 220 kV ou de ses composants, il convient de prendre en compte les éléments suivants :
- Demande de charge: Choisir la capacité en fonction des prévisions de charge de pointe et futures.
- Disponibilité de l'espace: Utiliser les SIG lorsque le terrain est limité.
- Conditions environnementales: La poussière, l'humidité, l'activité sismique peuvent avoir un impact sur la conception.
- Automatisation et surveillance: Les sous-stations modernes devraient prendre en charge le SCADA et le contrôle basé sur l'IoT.
- Conformité: Garantir des normes telles que IEC 62271, IEEE C37et les codes locaux des services publics sont respectés.
Des fabricants réputés comme ABB, Siemens, Schneider Electricet PINEELE offrent des solutions modulaires de 220 kV conformes aux spécifications internationales.
Citer des sources autorisées
- IEEE : Systèmes d'alimentation électrique
- Solutions ABB pour les postes 220kV
- Wikipedia - Poste électrique
- Rapports de l'IEEMA
Section FAQ
Une sous-station de 220 kV relie les lignes de transmission à haute tension aux réseaux de distribution régionaux, permettant la transformation de la tension et la protection du système.
Les postes SIG économisent de l'espace, sont plus fiables dans les environnements difficiles et nécessitent moins d'entretien que les systèmes AIS.
220 kV fonctionne à un niveau plus élevé solutions de tensionLe réseau de 132 kV, qui supporte une charge plus importante, est généralement utilisé dans la couche de transmission du réseau, tandis que le réseau de 132 kV est davantage utilisé pour la sous-transmission ou la distribution.
Conclusion
Le Sous-station 220 kV est un élément essentiel du réseau moderne de transport d'électricité. Il garantit que l'électricité produite par les centrales électriques est transmise efficacement sur de longues distances et qu'elle est ensuite abaissée pour être utilisée par l'industrie ou le public. Il est essentiel pour les ingénieurs, les planificateurs des services publics et les équipes chargées des achats de comprendre les critères de conception, d'application et de sélection de cet élément afin de maintenir la stabilité du réseau et de répondre à la demande croissante d'énergie.


