- Concepto básico: ¿Qué es una pequeña subestación?
- Aplicaciones de las pequeñas subestaciones
- Tendencias del mercado y antecedentes
- Especificaciones técnicas
- Pequeñas y grandes subestaciones: ¿Cuál es la diferencia?
- Consejos de compra: Cómo elegir una subestación pequeña
- Fuentes citadas y recomendadas
- Preguntas frecuentes
Concepto básico: ¿Qué es una pequeña subestación?
A pequeña subestación-también conocido como subestación compacta o minisubestación-es una unidad de distribución de energía totalmente integrada que incluye:
- Aparamenta de media tensión
- Transformador de distribución
- Panel de baja tensión
- Todo dentro de una carcasa resistente a la intemperie, montada en fábrica
Estas subestaciones suelen gestionar De 100 kVA a 2500 kVA y operar dentro de Sistemas de 11 kV, 22 kV o 33 kV. Su diseño compacto y "plug and play" permite una instalación rápida y una obra civil mínima, por lo que son ideales para zonas urbanas y rurales de rápido crecimiento.
Aplicaciones de las pequeñas subestaciones
Las subestaciones pequeñas se utilizan mucho en:
- Edificios residenciales y comerciales
Reducción de tensión a 400 V para uso doméstico o de oficina - Polígonos industriales
Alimentación de maquinaria a pequeña escala o unidades de proceso locales - Plantas de energía renovable
Actuar como punto de interconexión entre los parques solares o eólicos y la red pública - Unidades móviles de energía
Se utiliza en minería, yacimientos petrolíferos y proyectos de construcción temporales - Electrificación rural o remota
Llevar energía a zonas donde la expansión de la red es limitada
Tendencias del mercado y antecedentes
Según IEEMA y AIE informes, la demanda de pequeñas subestaciones está aumentando en todo el mundo debido a:
- Rápida urbanización y programas de electrificación rural
- Crecimiento de las instalaciones solares en tejados y microrredes
- Mayor dependencia de los sistemas de energía distribuida
- Proyectos de desarrollo de ciudades inteligentes
Las subestaciones pequeñas, sobre todo las prefabricadas y las montadas sobre patines, son un componente clave de los sistemas de transporte. estrategias energéticas descentralizadasque proporcionan una energía local fiable sin tener que recurrir a subestaciones de gran tamaño.
Según WikipediaLas subestaciones compactas forman parte de un esfuerzo más amplio por mejorar la eficiencia energética y reducir las pérdidas en el último tramo.
Especificaciones técnicas
| Componente | Rango / Valor típico |
|---|---|
| Tensión nominal | 11kV / 22kV / 33kV |
| Capacidad del transformador | 100 - 2500 kVA |
| Tensión de salida BT | 400V / 415V |
| Frecuencia | 50Hz / 60Hz |
| Clase de protección | IP44 - IP65 |
| Tipo de caja | Exterior con revestimiento metálico o tipo quiosco |
| Tipo de refrigeración | Transformador sumergido en aceite o seco |
| Cumplimiento de las normas | IEC 62271, IEC 60076, IEEE C57 |
Pequeñas y grandes subestaciones: ¿Cuál es la diferencia?
| Característica | Pequeña subestación | Subestación grande |
|---|---|---|
| Capacidad de potencia | 100 - 2500 kVA | Más de 5000 kVA |
| Niveles de tensión | Hasta 33 kV | Hasta 400 kV o más |
| Huella | Compacto (1-3 m²) | Gran superficie (varios edificios) |
| Tiempo de instalación | 1-2 días | Semanas o meses |
| Aplicaciones | Distribución local | Control regional de la red |
| Personalización | Limitado | Altamente personalizable |
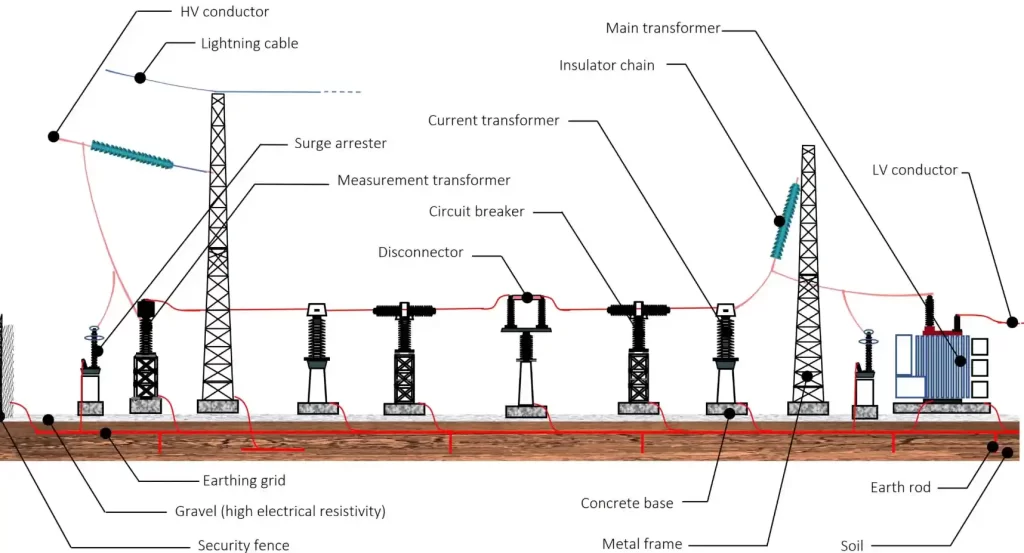
Consejos de compra: Cómo elegir una subestación pequeña
A la hora de elegir una subestación pequeña, ten en cuenta:
- Requisito de carga: Determine el tamaño del transformador en función de la carga máxima (en kVA).
- Medio ambiente: Elija una caja con clasificación IP54+ para zonas polvorientas o húmedas.
- Tipo de transformador:
- En aceite: Más eficaz y rentable
- Tipo seco: Más seguro en interiores y para zonas sensibles al fuego
- Sistemas de protección: Asegúrese de que el cuadro de baja tensión incluye disyuntores magnetotérmicos, protectores contra sobretensiones y contadores.
- Movilidad: Para uso temporal, las unidades montadas sobre patines o remolques son ideales.
Proveedores reputados como ABB, Schneider Electric, Siemensy fabricantes emergentes como PINEELE ofrecen una amplia gama de subestaciones compactas con certificación IEC/ANSI.
Fuentes citadas y recomendadas
- Serie IEEE C57 - Normas para transformadores
- Wikipedia: Subestación eléctrica
- Subestaciones secundarias compactas ABB
- Informes IEEMA - Desarrollo de subestaciones en la India
Preguntas frecuentes
A: Con un mantenimiento adecuado, las subestaciones pequeñas pueden durar entre 25 y 30 años, dependiendo de las condiciones ambientales y la calidad de los componentes.
A: Sí, se utilizan habitualmente para subir o bajar la tensión en sistemas solares fotovoltaicos y son ideales para aplicaciones de energía híbrida.
A: La mayoría de las unidades son montado en fábrica y se entregan listos para su uso. Se colocan con una grúa y se conectan en cuestión de horas, minimizando el trabajo en la obra.
A pequeño guía de subestaciones es algo más que una versión en miniatura de un concentrador eléctrico convencional: es una solución muy práctica, eficiente y escalable para la distribución moderna de electricidad. Ya sea para una urbanización, una huerta solar o un emplazamiento industrial temporal, las subestaciones compactas constituyen la columna vertebral de los sistemas energéticos localizados.
Al conocer los componentes, las normas y las opciones de configuración, los ingenieros y responsables de la toma de decisiones pueden elegir la solución adecuada que equilibre coste, rendimiento y fiabilidad.


